Configuration options for the Gateway agent type
- Settings
- TLS/SSL Interception
- Bypass Categories
- Captive / Guest Portal
- Gateway Anti-Malware
- Image Analysis
The Agent Configuration screen allows you to create or modify agent profiles for Gateway agents. Selecting a Gateway agent profile from the list will allow you to configure the profile.
To see the different Agent Configuration profiles attached to your account, visit your USS Dashboard and click Products ⟶ Web Security ⟶ Agent Configuration.
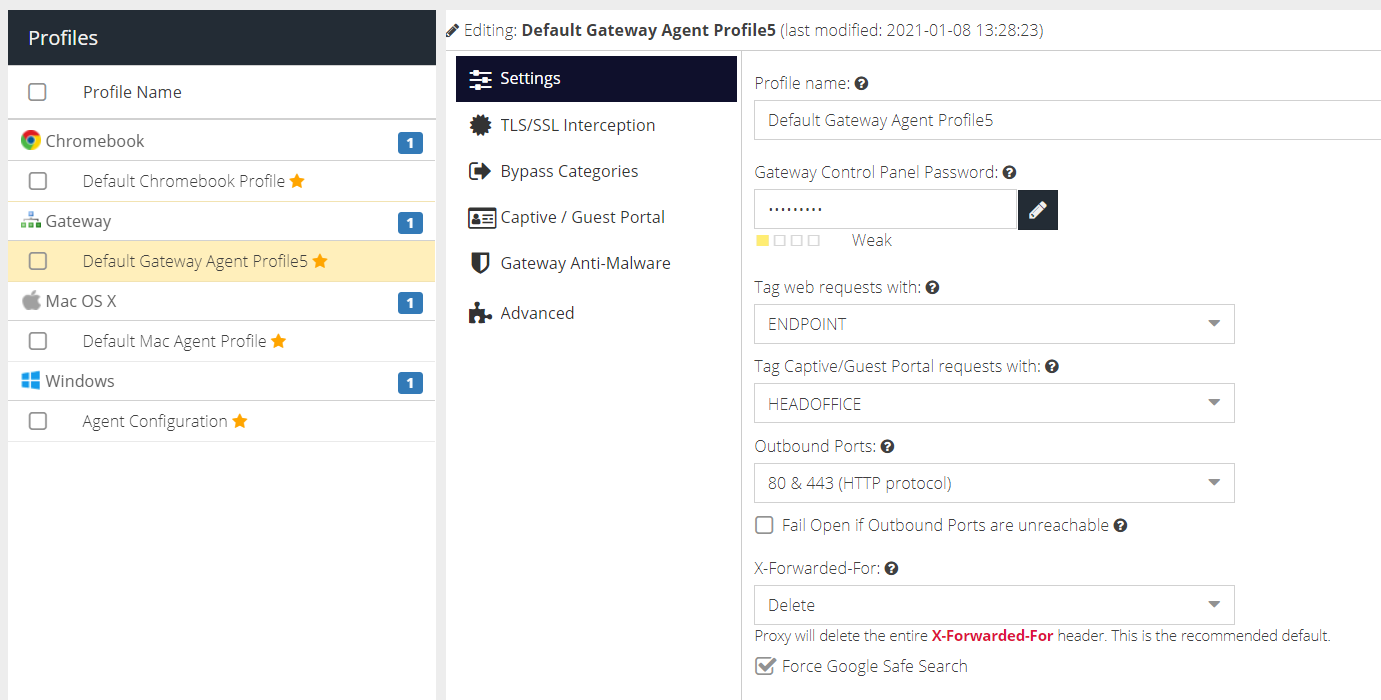
Settings
Profile name
A friendly name for the profile to make it easier to manage.
Gateway Control Panel Password
This password secures access to the Web UI on the gateway server. This password is automatically generated when the profile is created but can be changed.
Tag web requests with
The Tag to assign to this agent. Tags are used to identify the agent in Filter Rules. Select a tag to use, or choose No Selection if a tag is not required.
Tag Captive/Guest Portal requests with
The Tag to assign to traffic when the gateway is used as a transparent proxy e.g. with Captive or Guest portal. Tags are used to identify the traffic in Filter Rules. Select a tag to use or No Selection if a tag is not required.
Outbound ports
The agent will connect to the Web Security cloud service on ports 1344 & 1345 or 80 & 443. Select the preferred ports here and they will be tried first. If a connection is not established, the agent will try the remaining ports.
Fail open if Outbound Ports are unreachable
If enabled, the agent will provide unfiltered access if for any reason the Web Security cloud service ports are inaccessible. If not enabled, web access will be blocked until the cloud service becomes available again.
X-Forwarded-For
Determines how the proxy will handle the X-Forwarded-For header. The default option is to remove it completely. The options are:
On | Proxy will append the client IP address in the HTTP requests it forwards. By default it looks like: X-Forwarded-For: 192.1.2.3 |
Off | Proxy will change the header to appear as X-Forwarded-For: unknown |
Transparent | Proxy will not alter the X-Forwarded-For header in any way |
Delete | Proxy will delete the entire X-Forwarded-For header. This is the recommended default |
Truncate | Proxy will remove all existing X-Forwarded-For entries, and place the client IP as the sole entry |
TLS/SSL Interception
TLS/SSL Intercept on direct proxy connections
Force TLS/SSL decryption and filtering on direct connections to the proxy on port 8080 e.g. via browser configuration or WPAD.
TLS/SSL Intercept on transparent proxy (Captive/Guest Portal) connections
Force TLS/SSL decryption and filtering on transparently proxied connections e.g. Captive/Guest portal, WCCP, gateway mode.
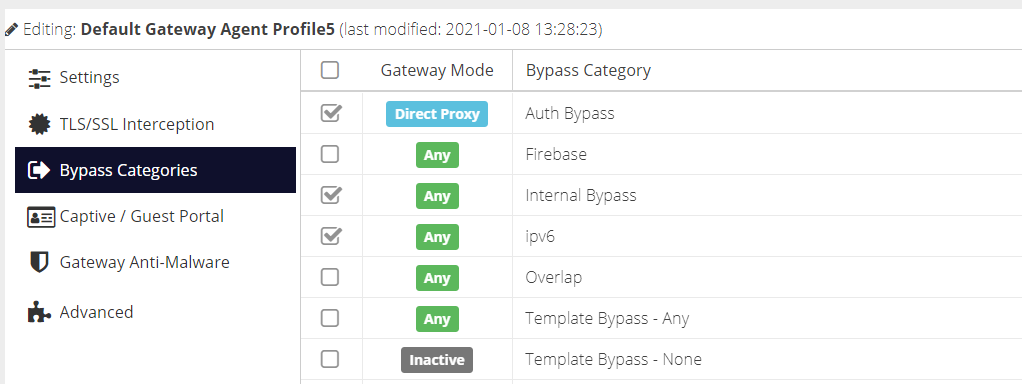
Bypass Categories
The Bypass Categories section contains a list of available categories, created in the Bypass section of the Web Security product. Bypass categories provide a way for the gateway to trust particular network resources, so that matching traffic does not get filtered by the Web Security cloud service. A number of pre-defined categories are provided as a starting point for common services.
Captive / Guest Portal
The Captive and Guest Portals provide an easy way to handle Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) and Guest (Anonymous) browsing and form an important part of deployment.
In a BYOD scenario, the device (smartphone, tablet, laptop, etc) is owned by the employee and as such the IT department typically has no control over the configuration, nor do they want to get involved in changing it. In a Guest scenario, such as public Internet access area, the device is not owned by the company operating the network, the user of the device does not have any credentials and the IT department has no control over the configuration of the device. The Captive or Guest Portal provides a zero-configuration method to allow the device to join the network and browse the web securely, whilst still enforcing the correct policy for the staff member or generic policy for guest users.
How It Works
The Gateway server can be deployed in a Layer 3 transparent mode. The client devices need to have their default gateway set to the IP address of the Gateway server. When the client device makes an HTTP(s) request, the Gateway will intercept that request and display either a Captive Portal page or a Guest Portal page.
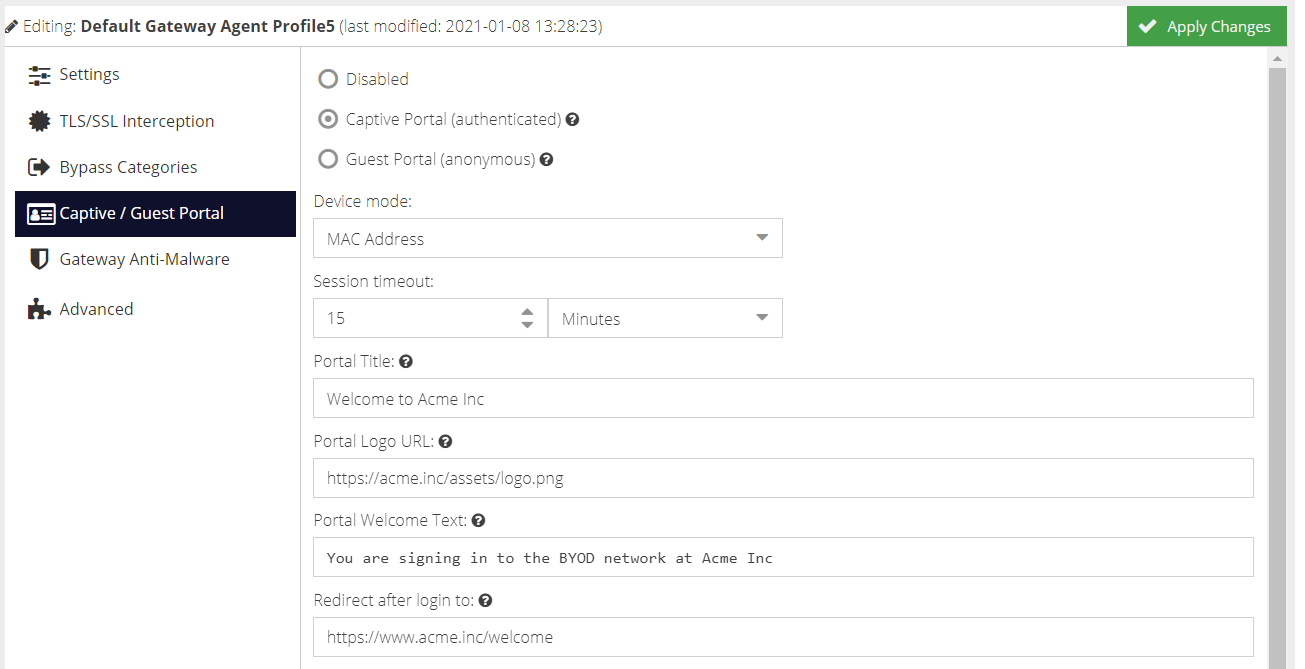
The Captive Portal page allows the user to authenticate against the configured Active Directory environment so that the administrator can apply user-based filtering and capture the username within the analytics reports.
The Guest Portal page is designed for public or anonymous access, where the user can accept the Terms of Service before being allowed to connect to the Internet via HTTP(s).
Once the client device has been accepted through either the Captive or Guest Portal, the request will be processed by the Gateway based on the policy configured in the Web Security filtering rules.
There are two types of portal available: Captive and Guest.
Captive Portal
The Captive Portal present a login page which requires a valid Active Directory username and password to proceed.
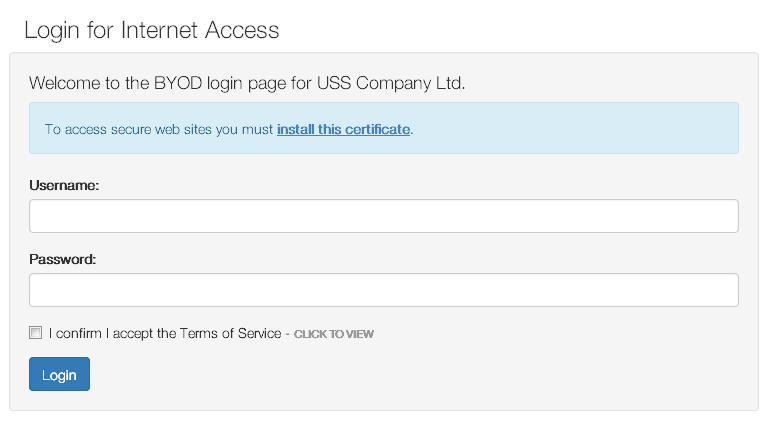
The logo, title, welcome text, acceptance checkbox and terms of service link can all be customised.
Guest Portal
The Guest Portal presents a splash screen which requires acceptance in order to proceed. No authentication is required.
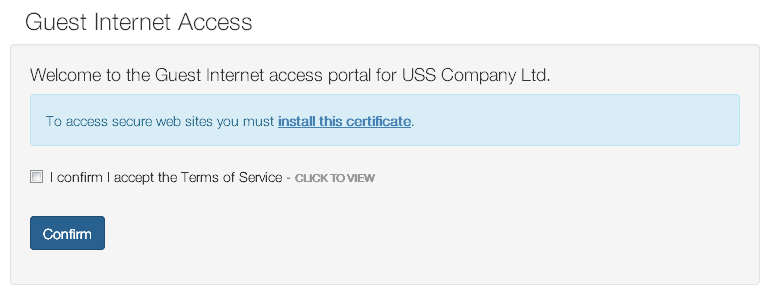
The title and welcome text can be customised. The logo, acceptance checkbox text and terms of service link are all inherited from the Captive Portal settings.
Deploying a Captive or Guest Portal
- Enable the Captive or GuestPortal in the Configuration Profile.
- Decide whether you require SSL/TLS Interception for the Captive/Guest Portal.
- Modify your DHCP server to issue the IP address of any of the configured network interfaces as the default gateway for the BYOD device.
- Re-join the BYOD device to the network so that it obtains a new DHCP lease and the correct default gateway.
- If SSL/TLS Intercept is enabled for the Captive/Guest Portal, install the SSL Certificate by clicking on the "install this certificate" link on the Captive / Guest portal page or by distributing the certificate via MDM to client devices.
- It is possible to selectively bypass SSL/TLS Interception for source IP addresses (devices) and destination domains
- It is possible to have SSL/TLS Interception on for direct proxy connections and off for Captive/Guest Portal
- If SSL/TLS Intercept is disabled for the Captive/Guest Portal, it is essential that the device is disconnected and reconnected to the WiFi network after changing its gateway IP address. HTTPS sites will not work until a session is established via step 4 above.
Gateway Anti-Malware
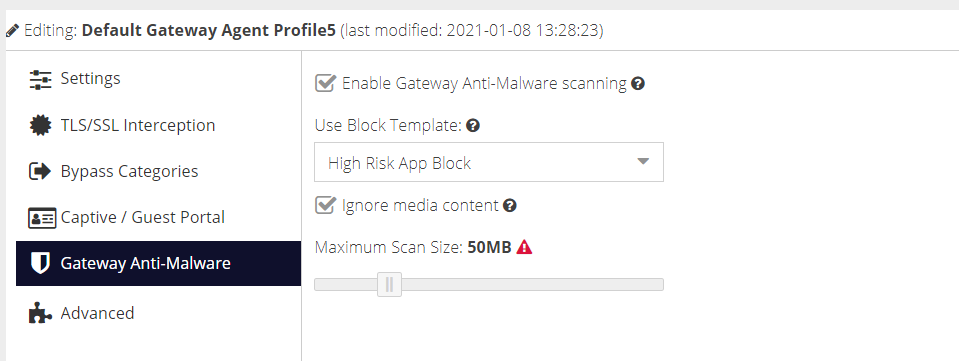
Enable Gateway Anti-Malware scanning
Check this box to enable the feature on the gateway's that are configured to use this configuration profile.
Use Block Template
Select a Web Security template to use if malware is detected.
Ignore Media Content
Check this box to ignore content that cannot be scanned such as streaming video and audio.
Maximum scan size (Mb)
The maximum file size that will be scanned for malware.
Image Analysis
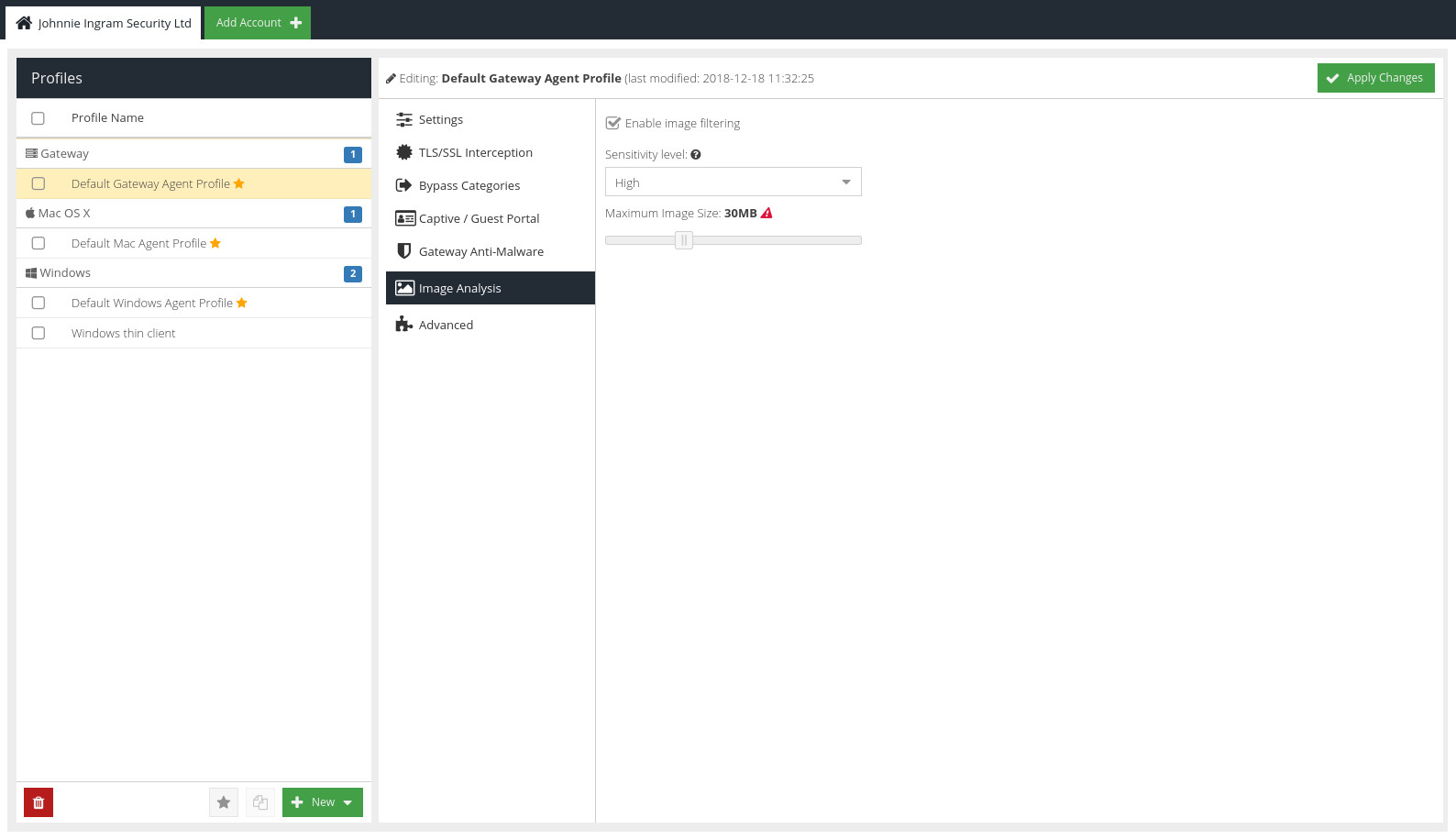
Enable image filtering
Check this box to enable the feature on the gateway's that are configured to use this configuration profile.
Sensitivity level
This option controls how aggressive the image scanner should be when trying to detect adult content.
Low
Only block images that are very likely to contain adult content (most accurate, less blocked).
Average
Block images that are very likely or moderately likely to contain adult content.
High
Block any images that are suspected of containing adult content (less accurate, more blocked)
The Image Scanner will assign a percentage score to each image that it scans which indicates a "certainty" that the image contains adult material. Changing the "Sensitivity level" adjusts the score at which the image is blocked. A "Low" sensitivity setting means the scanner won't block unless it is very certain that the image contains adult content. The end result is that fewer images will be blocked but the accuracy should be better. A "High" sensitivity setting means the scanner will block more because it will block even if it only suspects the image may contain adult content. The end result is that more images will be blocked but the accuracy will be reduced.
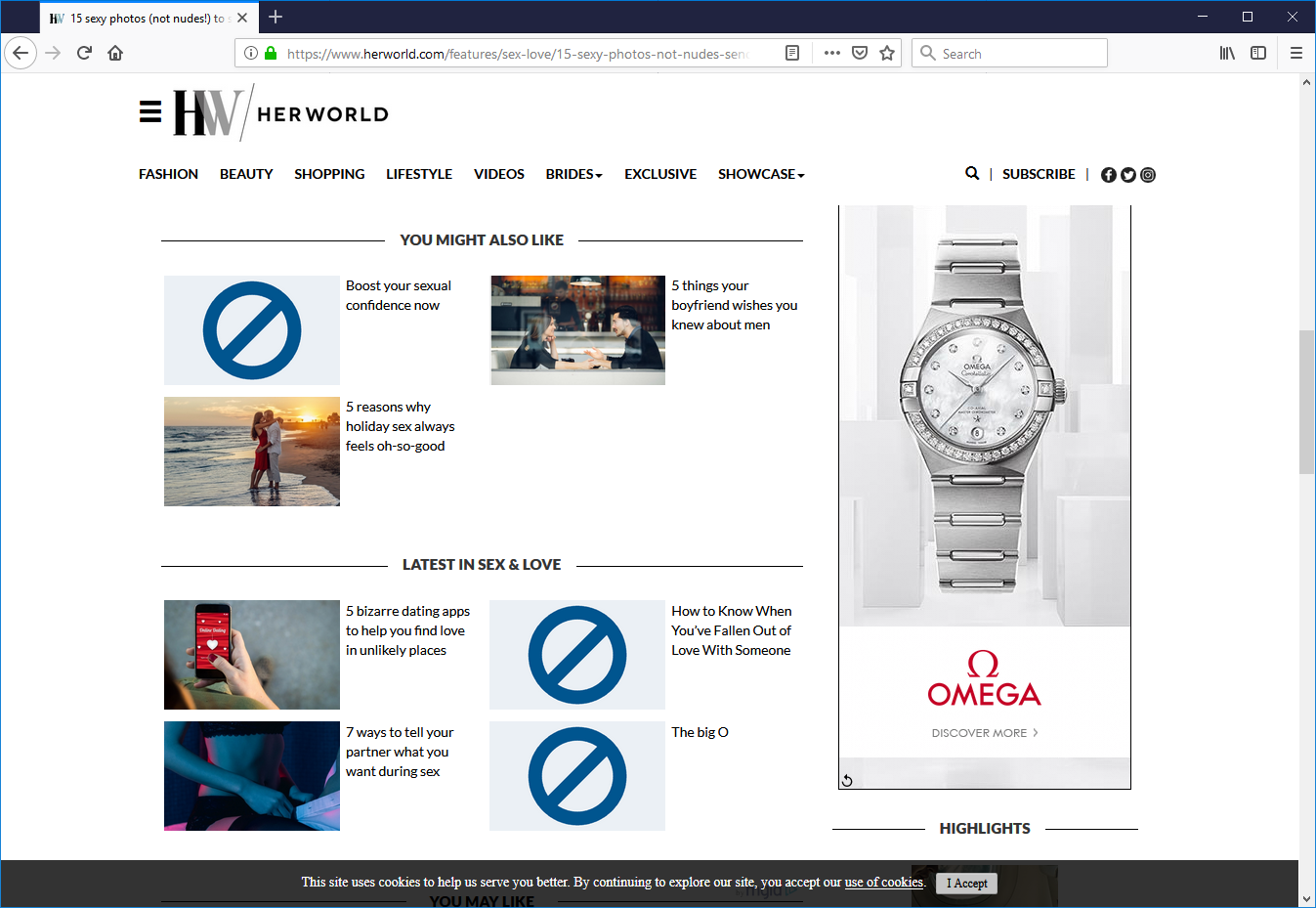
Example screenshot of the Image Scanner in action, with suspect images replaced by a safe symbol.
Maximum Image Size
The maximum filesize of an image to scan.
Advanced
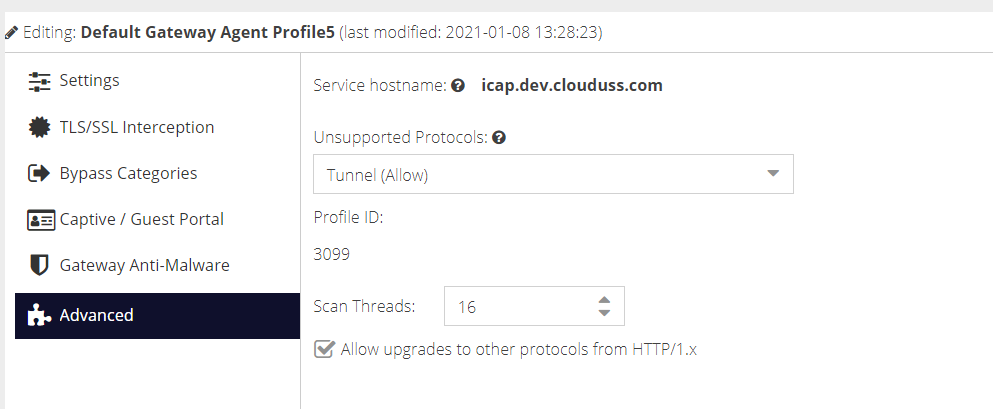
Service hostname
This is determined by the region chosen for the Web Security service.
Unsupported Protocols
This determines what the proxy should do if it encounters a non HTTP/S protocol. The default is to Deny, as any other protocols cannot be filtered and may pose a security risk.
Allow HTTP protocol upgrade
This determines whether the proxy will respect the HTTP Upgrade header, which is used by Web Sockets and HTTP 2.0 (see Wikipedia for more detail). The default is to deny the upgrade request as this could be used by any proprietary protocol which may lead to unacceptable risk. If you require Web Socket support then this option must be enabled.
If you intend to use Firefox 71+ with Web Sockets, please pay attention to this open and active bug.