WS - Rules Engine Concepts
At the core of the Web Security product is a flexible Rules Engine that determines how to control and monitor web activity. An understanding of the Rules Engine is important to get the most out of Web Security.
Rule types
The Rules Engine processes web activity by your users according to Rules defined in the Web Security product. Two types of Rule are available: Filter Rules and Feature Control Rules. Active Rules are applied to all web traffic captured by the deployed Agents for the given Unified Security Account.
Filter Rules
Filter Rules consist of
- Conditions: ways to identify web traffic
- Matches: what you're looking for in identified web traffic
- Actions: what to do with matched web traffic
Feature Control Rules
Just like a Filter Rule, a Feature Control Rule has Conditions and Matches. A Feature Control Rule is specific to a third-party web application, and can be used to permit, limit or deny features of that third-party application.
Rule Conditions
Both Filter Rules and Feature Control Rules always have at least one Condition, although a Rule can have more than one Condition.
Active Directory Username
The web traffic request must originate from at least one of the selected Active Directory users (based on sameaccountname, which is captured by an endpoint agent or network gateway).
Active Directory Organisational Unit
The web traffic request must originate from a user who is a member of at least one of the selected Organisational Units.
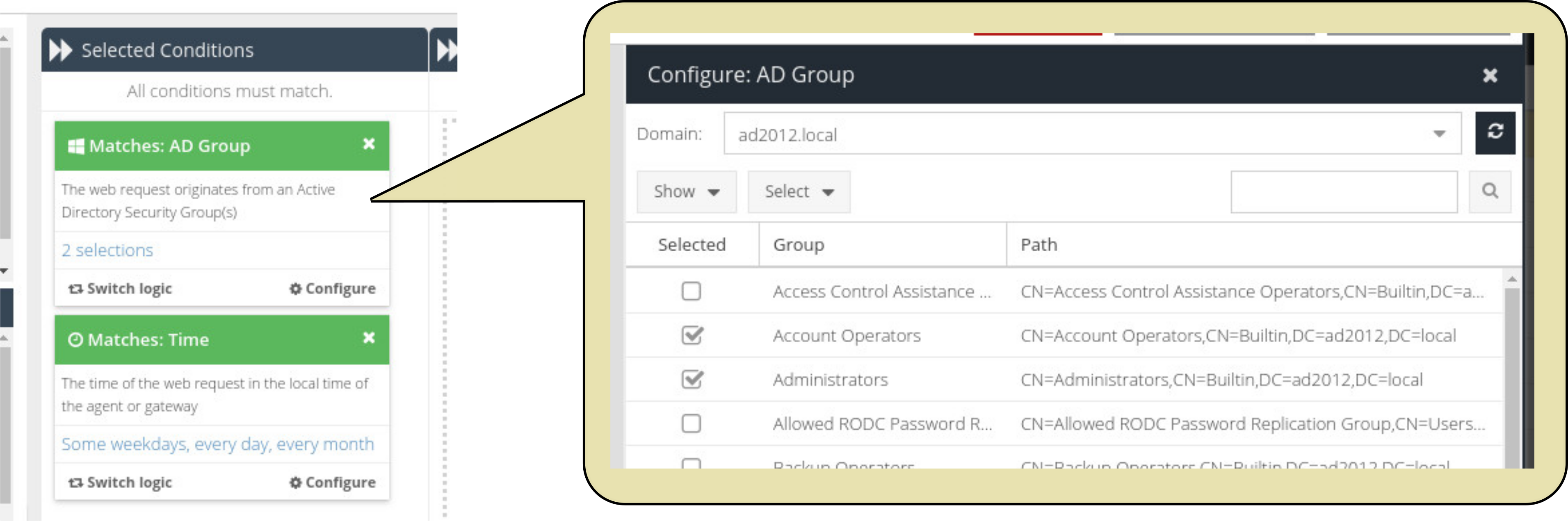
Active Directory Security Group
The web traffic request must originate from a user who is a member of at least one of the selected Security Groups.
Browser Type
The web traffic request must originate from a browser that matches one of the defined patterns in the Browser Category.
Device
The web traffic request must originate from either an IP address or MAC address of the selected device.
Device Group
The web traffic request must originate from either an IP address or a MAC address of a device belonging to the specified Device Group.
Device Type
The web traffic request must originate from one of the selected Device Types.
Operating System
The web traffic request must originated from one of the selected Operating Systems.
Tag
The web traffic request must be tagged with one of the selected Tags. Tags are applied to agents via Configuration Profiles.
Time
The web traffic request must have a timestamp that lies within the selected day of the week, day of the month, month, or specified time period(s). Times are stored in the system as UTC however the USS endpoint agent or network gateway captures the end-user timezone offset, which is used to calculate their local time and apply time periods to them correctly.
Rule Matches
Filter Rules and Feature Control Rules both use Matches, but the available Matches differ for each type of Rule.
Matches for Filter Rules
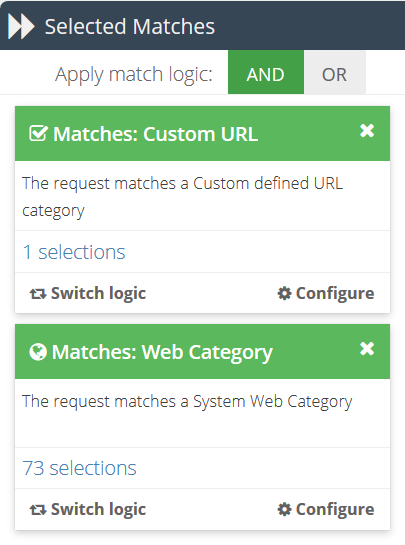
Web Category
The requested URL must be categorised in at least one of the selected web categories.
Custom URL
The requested URL must match a pattern found in at least one of the selected URL categories.
Keyword Category
The requested URL (or App Action Value, if the Cloud Application Security product is installed) must match a pattern in the selected Keyword Categories.
Read more about Keyword Categories
If the Cloud Application Security product is licensed, additional Matches will also be available:
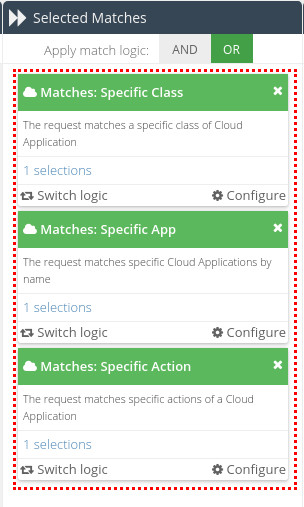
Specific Class
The requested App Action Value must be for an App that belongs to at least one of the selected Cloud Application classes (from the App Catalog). A class is essentially a grouping of apps by their type. For example, File Storage, Cloud CRM or IaaS.
Specific App
The requested App Action Value must be associated with at least one of the selected Apps from the App Catalog.
Specific Action
The requested App Action Value must be associated with at least one of the selected actions from Apps in the App Catalog.
Generic Action
The App Catalog contains thousands of actions across hundreds of apps, so to make this more manageable the actions are grouped into what is known as Generic Actions.
The requested App Action must be for at least one of the selected generic Cloud Application actions. Generic Actions apply across all apps in the App Catalog, rather than specific Apps. Examples of Generic Actions are uploading a file or posting a public message.
Cloud Risk Level
The request must be for a Cloud Application action that meets selected Risk Level. You can use the  toggle to choose whether the Match will trigger for requests below the selected Risk Level, or above it.
toggle to choose whether the Match will trigger for requests below the selected Risk Level, or above it.
Matches for Feature Control Rules
Google Safe Search
If the request is for a Google search engine result, enforce the strict Safe Search feature to block adult content. This will override the user's own preference settings.
Yahoo Safe Search
If the request is for a Yahoo! search engine result, enforce the strict Safe Search feature to block adult content. This will override the user's own preference settings.
Bing Safe Search
If the request is for a Bing search engine result, enforce the strict Safe Search feature to block adult content. This will override the user's own preference settings.
YouTube Safe Search
If the request is for a YouTube video search result, enforce the strict Safe Search feature to block adult content. This will override the user's own preference settings.
Network based enforcement may also be required through DNS. Please see this article for details.
YouTube for Schools
If the request is for a YouTube video search result, insert the YouTube For Schools header with the given token. This will cause the search to be executed as if it came from a YouTube For Schools account.
X-Youtube-Edu-Filter token to be able to correctly configure this Match.Google App Domain
If the request is for Google Apps, restrict the request to the specified domain.
X-Google-Apps-Allowed-Domains token to be able to correctly configure this Match. This token can simply consist of the domain(s) to which you want to restrict access. For example, mydomainname.com.Rule logic
Rules can consist of multiple Conditions, Matches and match values. When more than one options is chosen, Web Security uses intelligent logic to determine the correct way to proceed.
Rule logic for Conditions
Conditions use AND logic, which means that each Condition added to the Rule must be true. However, the options selected within each Condition use OR logic (meaning that the option will match if one or more of the selections are true.
Rule logic for Matches
In contrast to Conditions, Matches can use either AND or OR logic, depending on your requirements. Matches use OR logic by default.
Rule Actions
Rule Actions determine what should happen if the Conditions and Matches in the Rule are true.
When a Rule is first created, it will by default have an Action of Block, along with a Log Level Action of 'Normal'. You can easily add additional actions, or override these defaults, by dragging from the Actions panel to the Selected Actions column. There are several potential Actions available:
Allow
Allow the web request to proceed.
Block
Stop the web request. The user will instead be shown the specified HTML template.
Time Quota
If the user's Time Quota has not been exceeded, the web request is allowed to proceed, and the user's Time Quota is reduced accordingly. If the user's Time Quota has been exceeded, the final Action is automatically switched to a Block action.
Apply to
Determine exactly how the remaining Time Quota is calculated:
- User only: the quota is associated with the captured username. This user will be able to use the quota if they are logged in on other devices. The user must be synchronised from Active Directory.
- Device only: the quota is associated with the captured device (based on MAC address). Any user making a web request from that device will consume time from the same Quota. The Device must exist in the Devices section.
- User & Device: the warning is associated with the captured username and the captured device. Quota will only be consumed if both username and MAC address are present as described above. The user must be synchronised from Active Directory.
The default option is 'User & Device'.
Allow for (minutes)
The number of minutes for which the user is allowed to access the target site, after the Continue button is pressed. The minimum is 5 minutes, and the maximum is 23 hours 55 minutes.
Warn
The web request is stopped, and the user is instead shown the specified HTML template. If the template contains the placeholder text $WARN$, a Continue button will be available, so that the user can still access the blocked content if they deem it acceptable.
The Warn action can also be configured to require a password before the user is allowed to proceed.
Apply to
Determine exactly when the warning template is shown:
- User only: the warning is associated with the captured username. This user will be able to use the warning feature if they are logged in on other devices. The user must be synchronised from Active Directory.
- Device only: the warning is associated with the captured device (MAC address). Any user making a web request from that device will be able to use the warning feature. Requires Device Identification Mode to be set to MAC address.
- User & Device: the warning is associated with the captured username and the captured device. The warning feature will only be available if both username and MAC address are present. Requires Device Identification Mode to be set to MAC address. The user must be synchronised from Active Directory.
The default option is 'User & Device'.
Allow for (minutes)
The number of minutes for which the user is allowed to access the target site, after the Continue button is pressed. The minimum is 5 minutes, and the maximum is 23 hours 55 minutes.
Password
If a password is entered into this field, a user will not be allowed to proceed beyond the Warning page until the correct password is entered.
If you don't require a password, just leave the Password field blank.
Redirect
Stop the web request, and redirect the user to the specified URL.
Log Level
Choose the level of priority against which you want this web request to be logged. The default Log Level is 'Normal'.
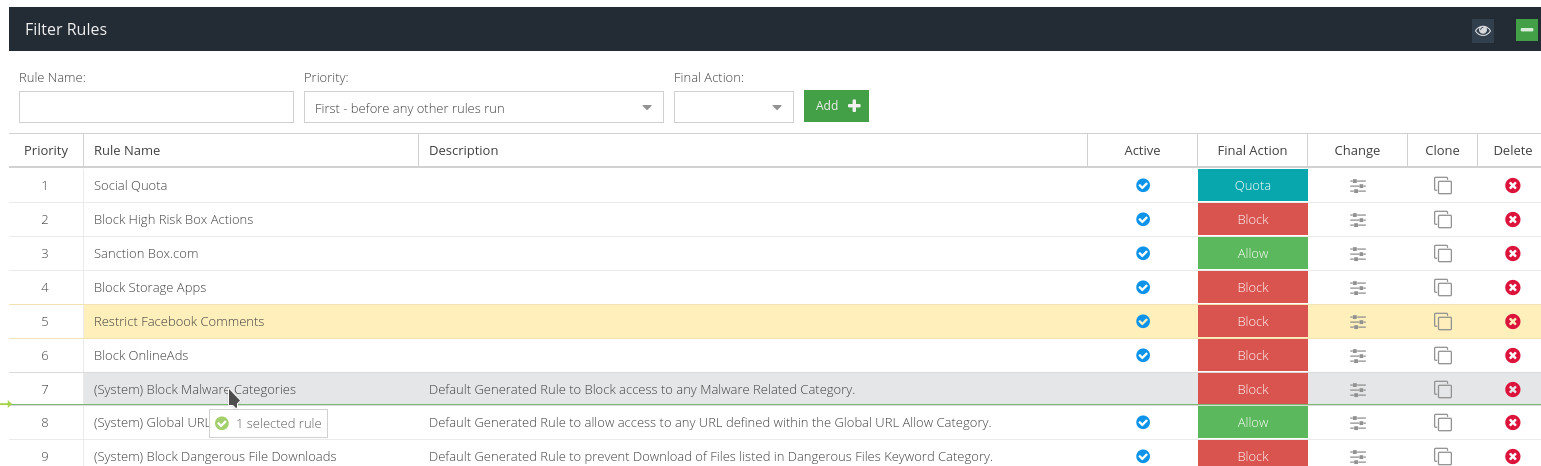
Rule Priority
The Rules Engine executes each Rule in turn, in the order they appear on the Filter Rules screen, from top to bottom. You can easily change the priority order by dragging and dropping.
Content Scan
Choose the Content Scan tile to select types of content that agents and Gateways should detect to match this action. The only currently supported type is "MIME Type" currently.
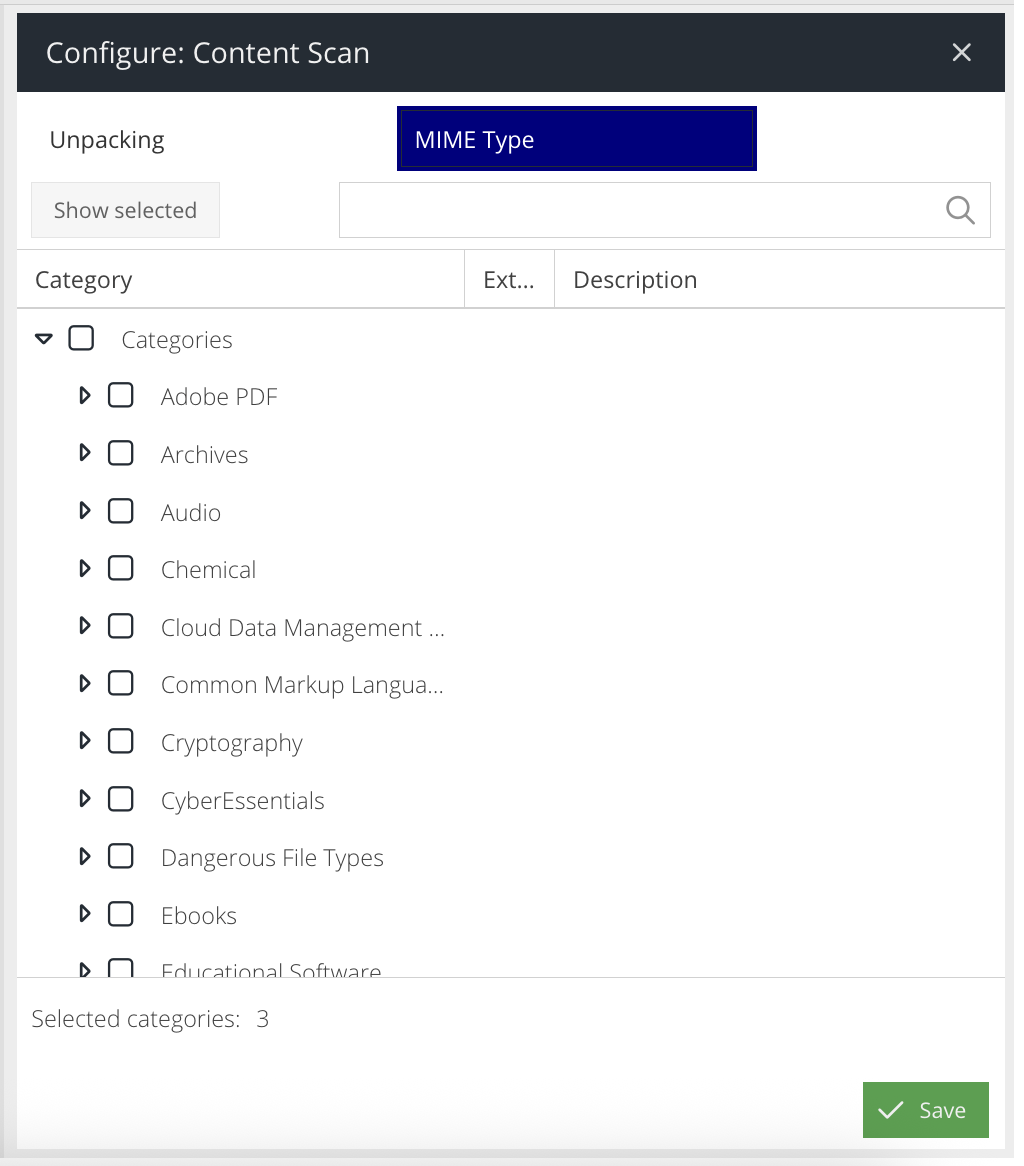
In addition, it is possible to enable automatic unpacking of archives to scan for MIME types within them. The unpacking engine supports the same archives as is listed in the "Archives" MIME type category.
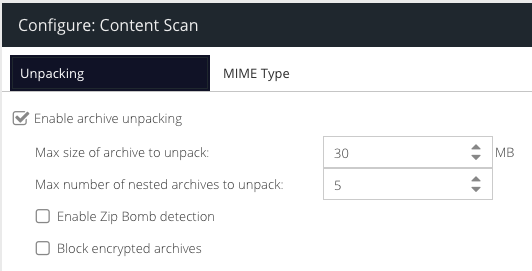
- Enable archive unpacking - tick this to enable the unpacking feature
- Max size of archive to unpack - the maximum size of the archive that will be unpacked. Increasing this number significantly will require additional memory resource. For the agent, set this to the maximum file size you want to scan. For the gateway, this is the size of the file to be captured in order to attempt classification.
- Max number of nested archives to unpack - the number of nested archives that will be unpacked before the unpacker engine gives up. For example, a zip within a zip within a zip.
- Enable Zip Bomb detection - this option will attempt to prevent Zip Bomb / Zip of Death files which are designed to consume all available disk space on the target machine. This option attempts to protect the system from this kind of file being opened.
- Block Encrypted Archives - blocks encrypted or password protected zip files and other compatible archives. Coming soon.
Template
Use this Action in conjunction with other actions such as Warn, Time Quota or Block. The Template action indicates which pre-defined HTML Template should be shown to the user.
Request versus Response scanning
An Action can either be "request-based" - in which case the Action is performed on the user's web request as it's made - or "response-based" (in which case the Action is performed against the web response that is returned when the user's web request has been carried out.
- A request-based Action will be indicated with a
 icon.
icon. - A response-based Action will be indicated with a
 icon.
icon.